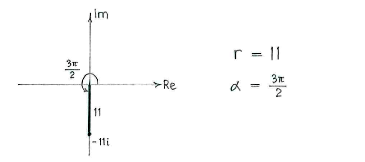Lösung 3.2:6b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
If we determine the number's magnitude <math>r</math> and argument <math>\alpha </math>, we can write its polar form using the formula | If we determine the number's magnitude <math>r</math> and argument <math>\alpha </math>, we can write its polar form using the formula | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>r(\cos\alpha + i\sin\alpha)\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
Because the number lies on the imaginary axis, it is possible to write its magnitude and argument directly. | Because the number lies on the imaginary axis, it is possible to write its magnitude and argument directly. | ||
The polar form is | The polar form is | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>11\Bigl(\cos\frac{3\pi}{2} + i\sin\frac{3\pi}{2}\Bigr)\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
Version vom 13:09, 10. Mär. 2009
If we determine the number's magnitude \displaystyle r and argument \displaystyle \alpha , we can write its polar form using the formula
| \displaystyle r(\cos\alpha + i\sin\alpha)\,\textrm{.} |
Because the number lies on the imaginary axis, it is possible to write its magnitude and argument directly.
The polar form is
| \displaystyle 11\Bigl(\cos\frac{3\pi}{2} + i\sin\frac{3\pi}{2}\Bigr)\,\textrm{.} |