Lösung 2.1:4a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
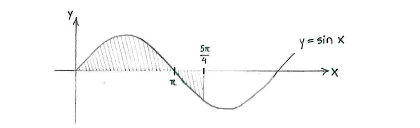
If we draw the curve \displaystyle y=\sin x, we see that the curve lies above the \displaystyle x -axis as far as \displaystyle x=\pi and then lies under the \displaystyle x -axis.
The area of the region between \displaystyle x=0 and \displaystyle x=\pi can therefore be written as
\displaystyle \int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\sin x}\,dx
whilst the area of the remaining region under the \displaystyle x -axis is equal to
\displaystyle -\int\limits_{\pi }^{{5\pi }/{4}\;}{\sin x}\,dx
(note the minus sign in front of the integral).
The total area becomes
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& \int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\sin x}\,dx-\int\limits_{\pi }^{{5\pi }/{4}\;}{\sin x}\,dx \\
& =\left[ -\cos x \right]_{0}^{\pi }-\left[ -\cos x \right]_{\pi }^{{5\pi }/{4}\;} \\
& =\left( -\cos \pi -\left( -\cos 0 \right) \right)-\left( -\cos \frac{5\pi }{4}-\left( -\cos \pi \right) \right) \\
& =\left( -\left( -1 \right)-\left( -1 \right) \right)-\left( -\left( -\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)-\left( -\left( -1 \right) \right) \right) \\
& =1+1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+1=3-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}
NOTE: a simple way to obtain the values of
\displaystyle \cos 0,
\displaystyle \cos \pi
and
\displaystyle \cos \frac{5\pi }{4}
is to draw the angles
\displaystyle 0,
\displaystyle \pi
and
\displaystyle \frac{5\pi }{4}
on a unit circle and to read off the cosine value as the
\displaystyle x
-coordinate for the corresponding point on the circle.