Lösung 3.2:4a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 3: | Zeile 3: | ||
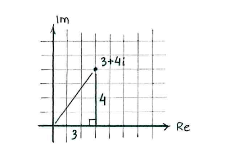
If we treat the line from the origin to <math>3+4i</math> as the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle which has its legs parallel with the real and imaginary axes, then the Pythagorean theorem gives that the magnitude is | If we treat the line from the origin to <math>3+4i</math> as the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle which has its legs parallel with the real and imaginary axes, then the Pythagorean theorem gives that the magnitude is | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>|3+4i| = \sqrt{3^2+4^2} = \sqrt{9+16} = \sqrt{25} = 5\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
[[Image:3_2_4_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:3_2_4_a.gif|center]] | ||
| Zeile 10: | Zeile 10: | ||
Note: In general, the magnitude of a complex number <math>z=x+iy</math> is equal to | Note: In general, the magnitude of a complex number <math>z=x+iy</math> is equal to | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>|z| = |x+iy| = \sqrt{x^2+y^2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
Version vom 13:08, 10. Mär. 2009
The magnitude of the number \displaystyle 3+4i is the number's distance to the origin in the complex number plane.
If we treat the line from the origin to \displaystyle 3+4i as the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle which has its legs parallel with the real and imaginary axes, then the Pythagorean theorem gives that the magnitude is
| \displaystyle |3+4i| = \sqrt{3^2+4^2} = \sqrt{9+16} = \sqrt{25} = 5\,\textrm{.} |
Note: In general, the magnitude of a complex number \displaystyle z=x+iy is equal to
| \displaystyle |z| = |x+iy| = \sqrt{x^2+y^2}\,\textrm{.} |