Lösung 3.2:4a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (Lösning 3.2:4a moved to Solution 3.2:4a: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
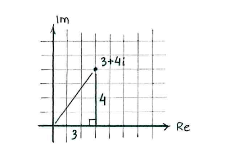
| - | {{ | + | The magnitude of the number |
| - | < | + | <math>\text{3}+\text{4}i</math> |
| - | {{ | + | is the number's distance to the origin in the complex number plane. |
| + | |||
| + | If we treat the line from the origin to | ||
| + | <math>\text{3}+\text{4}i</math> | ||
| + | as the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle which has its sides parallel with the real and imaginary axes, then Pythagoras' theorem gives that the magnitude is | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\left| \text{3}+\text{4}i \right|=\sqrt{3^{2}+4^{2}}=\sqrt{9+16}=\sqrt{25}=5</math> | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:3_2_4_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:3_2_4_a.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: In general, the magnitude of a complex number | ||
| + | <math>z=x+iy</math> | ||
| + | is equal to | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\left| z \right|=\left| x+iy \right|=\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}</math> | ||
Version vom 15:19, 22. Okt. 2008
The magnitude of the number \displaystyle \text{3}+\text{4}i is the number's distance to the origin in the complex number plane.
If we treat the line from the origin to \displaystyle \text{3}+\text{4}i as the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle which has its sides parallel with the real and imaginary axes, then Pythagoras' theorem gives that the magnitude is
\displaystyle \left| \text{3}+\text{4}i \right|=\sqrt{3^{2}+4^{2}}=\sqrt{9+16}=\sqrt{25}=5
NOTE: In general, the magnitude of a complex number \displaystyle z=x+iy is equal to
\displaystyle \left| z \right|=\left| x+iy \right|=\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}