Lösung 2.1:1a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
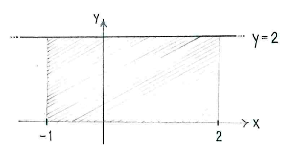
| - | The | + | The value of the integral can be interpreted as the area under the graph <math>y=2</math> from <math>x=-1\ </math> to <math>x=2</math>. |
| - | <math>y=2</math> | + | |
| - | from | + | |
| - | <math>x=-1\ </math> | + | |
| - | to | + | |
| - | <math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Image:2_1_1_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:2_1_1_a.gif|center]] | ||
| Zeile 12: | Zeile 5: | ||
Because the region is a rectangle, we can determine its area directly and obtain | Because the region is a rectangle, we can determine its area directly and obtain | ||
| - | + | {{Displayed math||<math>\int\limits_{-1}^{2} 2\,dx = \text{(base)}\cdot\text{(height)} = 3\cdot 2 = 6\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | |
| - | <math>\int\limits_{-1}^{2} | + | |
| - | (base) | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | (height) | + | |
| - | + | ||
Version vom 12:04, 21. Okt. 2008
The value of the integral can be interpreted as the area under the graph \displaystyle y=2 from \displaystyle x=-1\ to \displaystyle x=2.
Because the region is a rectangle, we can determine its area directly and obtain
| \displaystyle \int\limits_{-1}^{2} 2\,dx = \text{(base)}\cdot\text{(height)} = 3\cdot 2 = 6\,\textrm{.} |