Lösung 2.2:2a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
K (Lösning 2.2:2a moved to Solution 2.2:2a: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | {{ | + | The integral is a standard integral, with |
| - | < | + | <math>\text{5}x</math> |
| - | {{ | + | as the argument of the cosine function. If we therefore substitute |
| - | {{ | + | <math>u=\text{5}x</math>, we obtain the “correct” argument of the cosine, |
| - | < | + | |
| - | + | ||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & \int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\cos 5x\,dx=\left\{ \begin{array}{*{35}l} | ||
| + | u=\text{5}x \\ | ||
| + | du=\left( 5x \right)^{\prime }\,dx=5\,dx \\ | ||
| + | \end{array} \right\}} \\ | ||
| + | & =\frac{1}{5}\int\limits_{0}^{5\pi }{\cos u\,du} \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | As can be seen, the variable change replaced | ||
| + | <math>dx</math> | ||
| + | by | ||
| + | <math>\frac{1}{5}\,du</math> | ||
| + | and the new limits of integration become | ||
| + | <math>u=5\centerdot 0=0</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>u=5\centerdot \pi =5\pi </math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now, we have a standard integral which can easily compute: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & \frac{1}{5}\int\limits_{0}^{5\pi }{\cos u\,du}=\frac{1}{5}\left[ \sin u \right]_{0}^{5\pi } \\ | ||
| + | & =\frac{1}{5}\left( \sin 5\pi -\sin 0 \right)=\frac{1}{5}\left( 0-0 \right)=0 \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
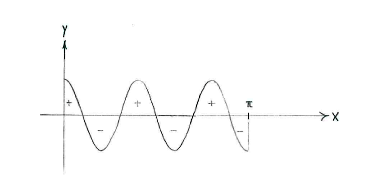
| + | NOTE: if we draw the graph for | ||
| + | <math>y=\cos 5x</math>, we see also that the area between the curve and | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis above the | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis is the same as the area under the | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis. | ||
[[Image:2_2_2_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:2_2_2_a.gif|center]] | ||
Version vom 10:07, 19. Okt. 2008
The integral is a standard integral, with \displaystyle \text{5}x as the argument of the cosine function. If we therefore substitute \displaystyle u=\text{5}x, we obtain the “correct” argument of the cosine,
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& \int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\cos 5x\,dx=\left\{ \begin{array}{*{35}l}
u=\text{5}x \\
du=\left( 5x \right)^{\prime }\,dx=5\,dx \\
\end{array} \right\}} \\
& =\frac{1}{5}\int\limits_{0}^{5\pi }{\cos u\,du} \\
\end{align}
As can be seen, the variable change replaced \displaystyle dx by \displaystyle \frac{1}{5}\,du and the new limits of integration become \displaystyle u=5\centerdot 0=0 and \displaystyle u=5\centerdot \pi =5\pi .
Now, we have a standard integral which can easily compute:
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& \frac{1}{5}\int\limits_{0}^{5\pi }{\cos u\,du}=\frac{1}{5}\left[ \sin u \right]_{0}^{5\pi } \\
& =\frac{1}{5}\left( \sin 5\pi -\sin 0 \right)=\frac{1}{5}\left( 0-0 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}
NOTE: if we draw the graph for
\displaystyle y=\cos 5x, we see also that the area between the curve and
\displaystyle x
-axis above the
\displaystyle x
-axis is the same as the area under the
\displaystyle x
-axis.