Lösung 1.3:1c
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
K (Solution 1.3:1c moved to Lösung 1.3:1c: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
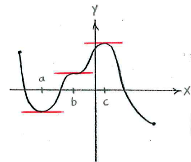
| - | + | Die Ableitung der Funktion hat drei Nullstellen, <math>x=a</math>, <math>x=b</math> und <math>x=c</math> (siehe Figur). Dies sind die stationären Punkte. | |
[[Image:1_3_1_c1.gif|center]] | [[Image:1_3_1_c1.gif|center]] | ||
| - | + | Der Punkt <math>x=b</math> ist ein Sattelpunkt nachdem die Ableitung links und rechts vom Punkt positiv ist. | |
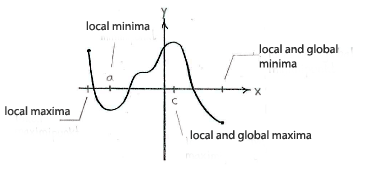
| - | + | Am linken Endpunkt, und im Punkt <math>x=c</math> hat die Funktion lokale Minima. Am rechten Endpunkt und im Punkt <math>x=a</math> hat die Funktion lokale Maxima. | |
| - | + | Von diesen Punkten ist <math>x=c</math> das globale Maxima, und der rechte Endpunkt das globale Minima. | |
[[Image:1_3_1_c2.gif|center]] | [[Image:1_3_1_c2.gif|center]] | ||
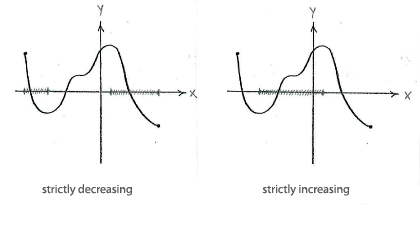
| - | + | Zwischen den linken Endpunkt und <math>x=a</math>, sowohl wie zwischen <math>x=c</math> und den rechten Endpunkt. ist die Funktion streng fallend, während die Funktion streng steigend zwischen <math>x=a</math> und <math>x=c</math> ist. | |
| - | + | ||
[[Image:1_3_1_c3.gif|center]] | [[Image:1_3_1_c3.gif|center]] | ||
Version vom 15:05, 26. Apr. 2009
Die Ableitung der Funktion hat drei Nullstellen, \displaystyle x=a, \displaystyle x=b und \displaystyle x=c (siehe Figur). Dies sind die stationären Punkte.
Der Punkt \displaystyle x=b ist ein Sattelpunkt nachdem die Ableitung links und rechts vom Punkt positiv ist.
Am linken Endpunkt, und im Punkt \displaystyle x=c hat die Funktion lokale Minima. Am rechten Endpunkt und im Punkt \displaystyle x=a hat die Funktion lokale Maxima.
Von diesen Punkten ist \displaystyle x=c das globale Maxima, und der rechte Endpunkt das globale Minima.
Zwischen den linken Endpunkt und \displaystyle x=a, sowohl wie zwischen \displaystyle x=c und den rechten Endpunkt. ist die Funktion streng fallend, während die Funktion streng steigend zwischen \displaystyle x=a und \displaystyle x=c ist.