Lösung 1.3:5
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
K (Lösning 1.3:5 moved to Solution 1.3:5: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
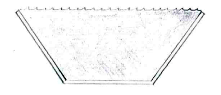
| - | + | The channel holds most water when its cross-sectional area is greatest. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Image:1_3_5_1_1.gif|center]] | [[Image:1_3_5_1_1.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
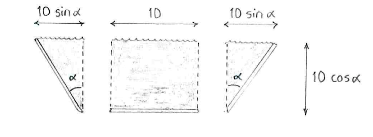
| + | By dividing up the channel's cross-section into a rectangle and two triangles we can, with the help of a little trigonometry, determine the lengths of the rectangle's and triangles' sides, and thence the cross-sectional area. | ||
[[Image:1_3_5_1_2.gif|center]] | [[Image:1_3_5_1_2.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The area of the cross-section is | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & A\left( \alpha \right)=10\centerdot 10\cos \alpha +2\centerdot \frac{1}{2}\centerdot 10\cos \alpha \centerdot 10\sin \alpha \\ | ||
| + | & =100\cos \alpha \left( 1+\sin \alpha \right) \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If we limit the angle to lie between | ||
| + | <math>0</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>{\pi }/{2}\;</math>, the problem can be formulated as : | ||
| + | |||
| + | Maximise the function | ||
| + | <math>A\left( \alpha \right)=100\cos \alpha \left( 1+\sin \alpha \right)</math> | ||
| + | when | ||
| + | <math>0\le \alpha \le {\pi }/{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | . | ||
| + | The area function is a differentiable function and the area is least when | ||
| + | <math>\alpha =0</math> | ||
| + | or | ||
| + | <math>\alpha ={\pi }/{2}\;</math>, so the area must assume its maximum at a critical point of the area function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We differentiate the area function: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & {A}'\left( \alpha \right)=100\centerdot \left( -\sin \alpha \right)\centerdot \left( 1+\sin \alpha \right)+100\centerdot \cos \alpha \centerdot \cos \alpha \\ | ||
| + | & =-100\sin \alpha -100\sin ^{2}\alpha +100\cos ^{2}\alpha \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | At a critical point | ||
| + | <math>{A}'\left( \alpha \right)=0</math> | ||
| + | and this gives us the equation | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\sin \alpha +\sin ^{2}\alpha -\cos ^{2}\alpha =0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | after eliminating the factor | ||
| + | <math>-100</math>. We replace | ||
| + | <math>\cos ^{2}\alpha </math> | ||
| + | with | ||
| + | <math>1-\sin ^{2}\alpha </math> | ||
| + | (according to the Pythagorean identity) to obtain an equation solely in | ||
| + | <math>\sin \alpha </math>, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & \sin \alpha +\sin ^{2}\alpha -\left( 1-\sin ^{2}\alpha \right)=0 \\ | ||
| + | & 2\sin ^{2}\alpha +\sin \alpha -1=0 \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is a second-degree equation in sin alpha and completing the square gives that | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & 2\left( \sin \alpha +\frac{1}{4} \right)^{2}-2\left( \frac{1}{4} \right)^{2}-1=0 \\ | ||
| + | & \left( \sin \alpha +\frac{1}{4} \right)^{2}=\frac{9}{16} \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math>, | ||
| + | |||
| + | and we obtain | ||
| + | <math>\sin \alpha =-\frac{1}{4}\pm \frac{3}{4}</math> | ||
| + | i.e. | ||
| + | <math>\sin \alpha =-1</math> | ||
| + | or | ||
| + | <math>\sin \alpha =\frac{1}{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The case | ||
| + | <math>\sin \alpha =-1</math> | ||
| + | is not satisfied for | ||
| + | <math>0\le \alpha \le {\pi }/{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\sin \alpha =\frac{1}{2}</math> | ||
| + | gives | ||
| + | <math>\alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;</math>. Thus | ||
| + | <math>\alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | is a critical point. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we summarize, we know therefore that the cross-sectional area has local minimum points at | ||
| + | <math>\alpha =0</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\alpha ={\pi }/{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | and that we have a critical point at . | ||
| + | <math>\alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;</math> | ||
| + | This critical point must be a maximum, which we can also show using the second derivative, | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & {A}''\left( \alpha \right)=-100\cos \alpha -100\centerdot 2\sin \alpha \centerdot \cos \alpha +100\centerdot 2\cos \alpha \centerdot \left( -\sin \alpha \right) \\ | ||
| + | & =-100\cos \alpha \left( 1+4\sin \alpha \right) \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | which is negative at | ||
| + | <math>\alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;</math>, | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & {A}''\left( \frac{\pi }{6} \right)=-100\cos \frac{\pi }{6}\centerdot \left( 1+4\sin \frac{\pi }{6} \right) \\ | ||
| + | & =-100\centerdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\centerdot \left( 1+4\centerdot \frac{1}{2} \right)<0 \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are no local maximum points other than | ||
| + | <math>\alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;</math>, which must therefore also be a global maximum. | ||
Version vom 10:31, 16. Okt. 2008
The channel holds most water when its cross-sectional area is greatest.
By dividing up the channel's cross-section into a rectangle and two triangles we can, with the help of a little trigonometry, determine the lengths of the rectangle's and triangles' sides, and thence the cross-sectional area.
The area of the cross-section is
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& A\left( \alpha \right)=10\centerdot 10\cos \alpha +2\centerdot \frac{1}{2}\centerdot 10\cos \alpha \centerdot 10\sin \alpha \\
& =100\cos \alpha \left( 1+\sin \alpha \right) \\
\end{align}
If we limit the angle to lie between
\displaystyle 0
and
\displaystyle {\pi }/{2}\;, the problem can be formulated as :
Maximise the function \displaystyle A\left( \alpha \right)=100\cos \alpha \left( 1+\sin \alpha \right) when \displaystyle 0\le \alpha \le {\pi }/{2}\; . The area function is a differentiable function and the area is least when \displaystyle \alpha =0 or \displaystyle \alpha ={\pi }/{2}\;, so the area must assume its maximum at a critical point of the area function.
We differentiate the area function:
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& {A}'\left( \alpha \right)=100\centerdot \left( -\sin \alpha \right)\centerdot \left( 1+\sin \alpha \right)+100\centerdot \cos \alpha \centerdot \cos \alpha \\
& =-100\sin \alpha -100\sin ^{2}\alpha +100\cos ^{2}\alpha \\
\end{align}
At a critical point
\displaystyle {A}'\left( \alpha \right)=0
and this gives us the equation
\displaystyle \sin \alpha +\sin ^{2}\alpha -\cos ^{2}\alpha =0
after eliminating the factor
\displaystyle -100. We replace
\displaystyle \cos ^{2}\alpha
with
\displaystyle 1-\sin ^{2}\alpha
(according to the Pythagorean identity) to obtain an equation solely in
\displaystyle \sin \alpha ,
\displaystyle \begin{align} & \sin \alpha +\sin ^{2}\alpha -\left( 1-\sin ^{2}\alpha \right)=0 \\ & 2\sin ^{2}\alpha +\sin \alpha -1=0 \\ \end{align}
This is a second-degree equation in sin alpha and completing the square gives that
\displaystyle \begin{align} & 2\left( \sin \alpha +\frac{1}{4} \right)^{2}-2\left( \frac{1}{4} \right)^{2}-1=0 \\ & \left( \sin \alpha +\frac{1}{4} \right)^{2}=\frac{9}{16} \\ \end{align},
and we obtain \displaystyle \sin \alpha =-\frac{1}{4}\pm \frac{3}{4} i.e. \displaystyle \sin \alpha =-1 or \displaystyle \sin \alpha =\frac{1}{2}
The case \displaystyle \sin \alpha =-1 is not satisfied for \displaystyle 0\le \alpha \le {\pi }/{2}\; and \displaystyle \sin \alpha =\frac{1}{2} gives \displaystyle \alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;. Thus \displaystyle \alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;
is a critical point.
If we summarize, we know therefore that the cross-sectional area has local minimum points at \displaystyle \alpha =0 and \displaystyle \alpha ={\pi }/{2}\; and that we have a critical point at . \displaystyle \alpha ={\pi }/{6}\; This critical point must be a maximum, which we can also show using the second derivative,
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& {A}''\left( \alpha \right)=-100\cos \alpha -100\centerdot 2\sin \alpha \centerdot \cos \alpha +100\centerdot 2\cos \alpha \centerdot \left( -\sin \alpha \right) \\
& =-100\cos \alpha \left( 1+4\sin \alpha \right) \\
\end{align}
which is negative at
\displaystyle \alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;,
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& {A}''\left( \frac{\pi }{6} \right)=-100\cos \frac{\pi }{6}\centerdot \left( 1+4\sin \frac{\pi }{6} \right) \\
& =-100\centerdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\centerdot \left( 1+4\centerdot \frac{1}{2} \right)<0 \\
\end{align}
There are no local maximum points other than \displaystyle \alpha ={\pi }/{6}\;, which must therefore also be a global maximum.