Lösung 2.2:2a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
(Ny sida: {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:2_2_2a-1(2).gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:2_2_2a-1(2).gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}}) |
|||
| (Der Versionsvergleich bezieht 9 dazwischen liegende Versionen mit ein.) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | {{ | + | Wenn wir die Substition <math>u=5x</math> ausführen, erhalten wir ein schon bekanntes Integral. |
| - | + | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\int\limits_0^{\pi} \cos 5x\,dx = \left\{\begin{align} |
| - | {{ | + | u &= 5x\\[5pt] |
| - | + | du &= (5x)'\,dx = 5\,dx | |
| - | + | \end{align}\right\} = \frac{1}{5}\int\limits_0^{5\pi} \cos u\,du</math>}} | |
| + | |||
| + | Hier haben wir <math>dx</math> mit <math>\tfrac{1}{5}\,du</math> ersetzt. Die Grenzen, die wir erhalten sind <math>u=5\cdot 0=0</math> | ||
| + | und <math>u=5\cdot \pi = 5\pi\,</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Wir erhalten das Integral | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\frac{1}{5}\int\limits_0^{5\pi} \cos u\,du = \frac{1}{5}\Bigl[\ \sin u\ \Bigr]_0^{5\pi} = \frac{1}{5}( \sin 5\pi -\sin 0) = \frac{1}{5}(0-0) = 0\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
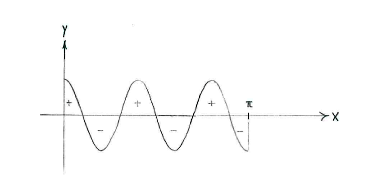
| + | Hinweis: Zeichnen wir die Graphe von <math>y=\cos 5x</math>, sehen wir, dass die gesamte Fläche oberhalb der ''x''-Achse genauso groß ist wie die gesamte Fläche unterhalb der ''x''-Achse ist. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2_2_2_a.gif|center]] | ||
Aktuelle Version
Wenn wir die Substition \displaystyle u=5x ausführen, erhalten wir ein schon bekanntes Integral.
| \displaystyle \int\limits_0^{\pi} \cos 5x\,dx = \left\{\begin{align}
u &= 5x\\[5pt] du &= (5x)'\,dx = 5\,dx \end{align}\right\} = \frac{1}{5}\int\limits_0^{5\pi} \cos u\,du |
Hier haben wir \displaystyle dx mit \displaystyle \tfrac{1}{5}\,du ersetzt. Die Grenzen, die wir erhalten sind \displaystyle u=5\cdot 0=0 und \displaystyle u=5\cdot \pi = 5\pi\,.
Wir erhalten das Integral
| \displaystyle \frac{1}{5}\int\limits_0^{5\pi} \cos u\,du = \frac{1}{5}\Bigl[\ \sin u\ \Bigr]_0^{5\pi} = \frac{1}{5}( \sin 5\pi -\sin 0) = \frac{1}{5}(0-0) = 0\,\textrm{.} |
Hinweis: Zeichnen wir die Graphe von \displaystyle y=\cos 5x, sehen wir, dass die gesamte Fläche oberhalb der x-Achse genauso groß ist wie die gesamte Fläche unterhalb der x-Achse ist.