Lösung 3.2:1d
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | + | If we calculate the expression, we get the answer at once, | |
| - | If we calculate the expression, we get the answer at once | + | |
| - | <math>\begin{align}z-\bar{w}+u &= (2+i)-(2-3i)+(-1-2i)\\ | + | {{Displayed math||<math>\begin{align} |
| - | &= 2-2-1+(1+3-2)i=-1+2i.\end{align}</math> | + | z-\bar{w}+u |
| + | &= (2+i)-(2-3i)+(-1-2i)\\[5pt] | ||
| + | &= 2-2-1+(1+3-2)i\\[5pt] | ||
| + | &= -1+2i\,\textrm{.} | ||
| + | \end{align}</math>}} | ||
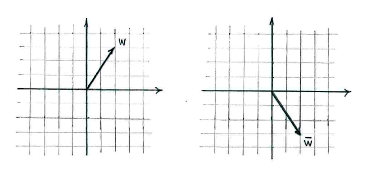
If, on the other hand, we interpret the expression in terms of vectors, we must first understand the vector <math>\bar{w}</math> geometrically. When we take the complex conjugate of <math>w</math>, we change the sign of the imaginary part, which is the same as reflecting <math>w</math> in the real axis. | If, on the other hand, we interpret the expression in terms of vectors, we must first understand the vector <math>\bar{w}</math> geometrically. When we take the complex conjugate of <math>w</math>, we change the sign of the imaginary part, which is the same as reflecting <math>w</math> in the real axis. | ||
| Zeile 12: | Zeile 15: | ||
[[Image:3_2_1d-2(2).gif|center]] | [[Image:3_2_1d-2(2).gif|center]] | ||
| - | {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} | ||
Version vom 09:31, 29. Okt. 2008
If we calculate the expression, we get the answer at once,
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
z-\bar{w}+u &= (2+i)-(2-3i)+(-1-2i)\\[5pt] &= 2-2-1+(1+3-2)i\\[5pt] &= -1+2i\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |
If, on the other hand, we interpret the expression in terms of vectors, we must first understand the vector \displaystyle \bar{w} geometrically. When we take the complex conjugate of \displaystyle w, we change the sign of the imaginary part, which is the same as reflecting \displaystyle w in the real axis.
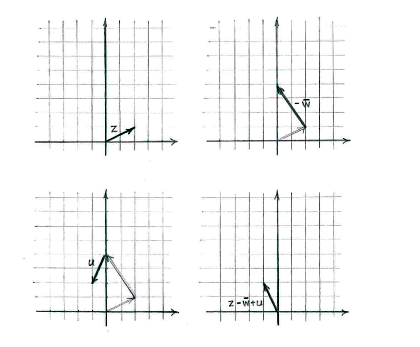
We can then construct the expression \displaystyle z-\bar{w}+u one term at a time.