Lösung 4.4:2d
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
K (Lösning 4.4:2d moved to Solution 4.4:2d: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
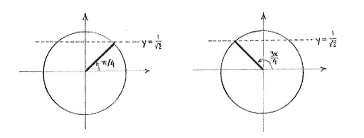
| - | {{ | + | Apart from the fact that there is a |
| - | < | + | <math>\text{5}x</math>, this is a normal trigonometric equation of the type |
| - | {{ | + | <math>\text{sin }y\text{ }=a</math> . If we are only interested in solutions which satisfy |
| - | { | + | <math>0\le \text{5}x\le \text{2}\pi </math>, then a sketch of the unit circle shows that there are two such solutions, |
| - | + | <math>\text{5}x=\text{ }\frac{\pi }{4}</math> | |
| - | {{ | + | and the reflectionally symmetric solution |
| + | <math>\text{5}x=\text{ }\pi \text{-}\frac{\pi }{4}=\frac{3\pi }{4}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:4_4_2_d.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_2_d.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | All of the equation's solutions are obtained from all values of 5x which differ by a multiple of 2π from either of these two solutions: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\text{5}x=\text{ }\frac{\pi }{4}+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\text{5}x=\frac{3\pi }{4}+2n\pi </math>, | ||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | <math>n</math> | ||
| + | is an arbitrary integer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we divide both of these by | ||
| + | <math>\text{5}</math>, we obtain the solutions expressed in terms of x alone: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x=\frac{\pi }{20}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi </math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>x=\frac{3\pi }{20}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi </math>, | ||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | <math>n</math> | ||
| + | is an arbitrary integer. | ||
Version vom 13:55, 30. Sep. 2008
Apart from the fact that there is a \displaystyle \text{5}x, this is a normal trigonometric equation of the type \displaystyle \text{sin }y\text{ }=a . If we are only interested in solutions which satisfy \displaystyle 0\le \text{5}x\le \text{2}\pi , then a sketch of the unit circle shows that there are two such solutions, \displaystyle \text{5}x=\text{ }\frac{\pi }{4} and the reflectionally symmetric solution \displaystyle \text{5}x=\text{ }\pi \text{-}\frac{\pi }{4}=\frac{3\pi }{4}.
All of the equation's solutions are obtained from all values of 5x which differ by a multiple of 2π from either of these two solutions:
\displaystyle \text{5}x=\text{ }\frac{\pi }{4}+2n\pi
and
\displaystyle \text{5}x=\frac{3\pi }{4}+2n\pi ,
where \displaystyle n is an arbitrary integer.
If we divide both of these by \displaystyle \text{5}, we obtain the solutions expressed in terms of x alone:
\displaystyle x=\frac{\pi }{20}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi
and
\displaystyle x=\frac{3\pi }{20}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi ,
where \displaystyle n is an arbitrary integer.