Lösung 4.1:5a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
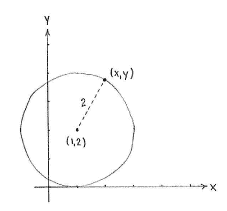
A circle is defined as all the points which have a fixed distance to the circle's midpoint. Hence, a point (''x'',''y'') lies on our circle if and only if its distance to the point (1,3) is exactly 2. Using the distance formula, we can express this condition as | A circle is defined as all the points which have a fixed distance to the circle's midpoint. Hence, a point (''x'',''y'') lies on our circle if and only if its distance to the point (1,3) is exactly 2. Using the distance formula, we can express this condition as | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\sqrt{(x-1)^2 + (y-2)^2} = 2\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
After squaring, we obtain the equation of the circle in standard form, | After squaring, we obtain the equation of the circle in standard form, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>(x-1)^2 + (y-2)^2 = 4\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
[[Image:4_1_5_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_1_5_a.gif|center]] | ||
Version vom 08:48, 22. Okt. 2008
A circle is defined as all the points which have a fixed distance to the circle's midpoint. Hence, a point (x,y) lies on our circle if and only if its distance to the point (1,3) is exactly 2. Using the distance formula, we can express this condition as
| \displaystyle \sqrt{(x-1)^2 + (y-2)^2} = 2\,\textrm{.} |
After squaring, we obtain the equation of the circle in standard form,
| \displaystyle (x-1)^2 + (y-2)^2 = 4\,\textrm{.} |