Solution 4.4:2b
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m (Lösning 4.4:2b moved to Solution 4.4:2b: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
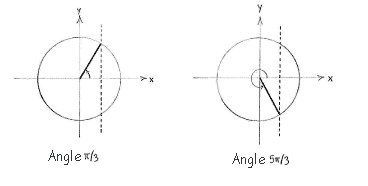
| - | {{ | + | The equation |
| - | < | + | <math>\cos x={1}/{2}\;</math> |
| - | {{ | + | has the solution |
| + | <math>x={\pi }/{3}\;</math> | ||
| + | in the first quadrant, and the symmetric solution | ||
| + | <math>x={2\pi -\pi }/{3}\;={5\pi }/{3}\;</math> | ||
| + | in the fourth quadrant. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:4_4_2_b.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_2_b.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Angle | ||
| + | <math>{\pi }/{3}\;</math> | ||
| + | Angle | ||
| + | <math>{5\pi }/{3}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If we add multiples of | ||
| + | <math>2\pi </math> | ||
| + | to these two solutions, we obtain all the solutions | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x={\pi }/{3}\;+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>x={5\pi }/{3}\;+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | <math>n</math> | ||
| + | is an arbitrary integer. | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 30 September 2008
The equation \displaystyle \cos x={1}/{2}\; has the solution \displaystyle x={\pi }/{3}\; in the first quadrant, and the symmetric solution \displaystyle x={2\pi -\pi }/{3}\;={5\pi }/{3}\; in the fourth quadrant.
Angle \displaystyle {\pi }/{3}\; Angle \displaystyle {5\pi }/{3}\;
If we add multiples of
\displaystyle 2\pi
to these two solutions, we obtain all the solutions
\displaystyle x={\pi }/{3}\;+2n\pi
and
\displaystyle x={5\pi }/{3}\;+2n\pi
where
\displaystyle n
is an arbitrary integer.