Solution 4.1:4a
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
m (Lösning 4.1:4a moved to Solution 4.1:4a: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | If we draw in the points in a coordinate system, we can see the line between the points as the hypotenuse in an imaginary right-angled triangle, where the opposite and adjacent are parallel with the | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | - and | ||
| + | <math>y</math> | ||
| + | -axes. | ||
| + | |||
{{NAVCONTENT_START}} | {{NAVCONTENT_START}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:4_1_4_a-1(2)_1.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_1_4_a-1(2)_1.gif|center]] | ||
| + | In this triangle, it is easy to measure the lengths of the opposite and the adjacent, which are simply the distances between the points in the | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | - | ||
| + | <math>y</math> | ||
| + | -directions. | ||
[[Image:4_1_4_a-1(2)_2.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_1_4_a-1(2)_2.gif|center]] | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
{{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} | {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using Pythagoras' theorem, we can then calculate the length of the hypotenuse, which is also the distance between the points: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\begin{align} | ||
| + | & d=\sqrt{\left( \Delta x \right)^{2}+\left( \Delta y \right)^{2}}=\sqrt{4^{2}+3^{2}} \\ | ||
| + | & =\sqrt{16+9}=\sqrt{25}=5 \\ | ||
| + | \end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: In general, the distance between two points | ||
| + | <math>\left( x \right.,\left. y \right)</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\left( a \right.,\left. b \right)</math> | ||
| + | is given by the formula | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>d=\sqrt{\left( x-a \right)^{2}+\left( y-b \right)^{2}}</math> | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 27 September 2008
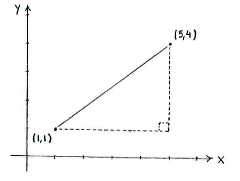
If we draw in the points in a coordinate system, we can see the line between the points as the hypotenuse in an imaginary right-angled triangle, where the opposite and adjacent are parallel with the \displaystyle x - and \displaystyle y -axes.
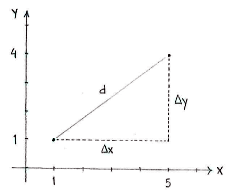
In this triangle, it is easy to measure the lengths of the opposite and the adjacent, which are simply the distances between the points in the \displaystyle x - \displaystyle y -directions.
Using Pythagoras' theorem, we can then calculate the length of the hypotenuse, which is also the distance between the points:
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& d=\sqrt{\left( \Delta x \right)^{2}+\left( \Delta y \right)^{2}}=\sqrt{4^{2}+3^{2}} \\
& =\sqrt{16+9}=\sqrt{25}=5 \\
\end{align}
NOTE: In general, the distance between two points
\displaystyle \left( x \right.,\left. y \right)
and
\displaystyle \left( a \right.,\left. b \right)
is given by the formula
\displaystyle d=\sqrt{\left( x-a \right)^{2}+\left( y-b \right)^{2}}