Lösung 4.4:2a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
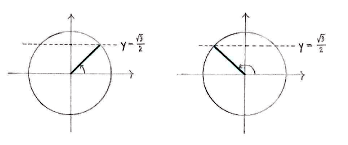
Wir zeichnen den Einheitskreis und markieren alle Winkel, die die 'y-Koordinate \displaystyle \sqrt{3}/2 haben. So erhalten wir alle Lösungen der Gleichung zwischen \displaystyle 0 und \displaystyle 2\pi.
Im ersten Quadranten wissen wir, dass \displaystyle x = \pi/3 den Sinus \displaystyle \sqrt{3}/2 hat. Noch dazu hat die Spiegelung an der y-Achse denselben Sinus, also ist \displaystyle x = \pi - \pi/3 = 2\pi/3 auch eine Lösung.
Addieren wir einen Vielfaches von \displaystyle 2\pi zu irgendeiner dieser Winkel, ändert sich deren Sinus nicht.
| \displaystyle x = \frac{\pi}{3}+2n\pi\qquad\text{und}\qquad x = \frac{2\pi}{3}+2n\pi\,, |
wobei n eine beliebige ganze Zahl ist.
Hinweis: Schreiben wir
| \displaystyle x = \frac{\pi}{3}+2n\pi\qquad\text{und}\qquad x = \frac{2\pi}{3}+2n\pi\,\textrm{,} |
heißt dies, dass die Gleichung für jedes n erfüllt ist, also für die Winkel
| \displaystyle \begin{array}{llll}
&n=0:\quad &x=\frac{\pi}{3}\quad &x=\frac{2\pi }{3}\\[5pt] &n=-1:\quad &x=\frac{\pi}{3}+(-1)\cdot 2\pi\quad &x=\frac{2\pi}{3}+(-1)\cdot 2\pi\\[5pt] &n=1:\quad &x=\frac{\pi}{3}+1\cdot 2\pi\quad &x=\frac{2\pi}{3}+1\cdot 2\pi\\[5pt] &n=-2:\quad &x=\frac{\pi}{3}+(-2)\cdot 2\pi\quad &x=\frac{2\pi}{3}+(-2)\cdot 2\pi\\[5pt] &n=2:\quad &x=\frac{\pi}{3}+2\cdot 2\pi\quad &x=\frac{2\pi}{3}+2\cdot 2\pi\\[5pt] &\phantom{n}\vdots &\phantom{x}\vdots &\phantom{x}\vdots \end{array} |