Lösung 4.4:5a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
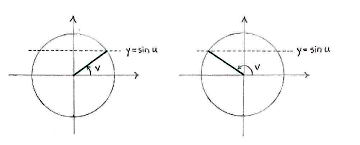
If we consider for a moment the equality
where u has a fixed value, there are usually two angles v in the unit circle which ensure that the equality holds,
(The only exception is when \displaystyle u = \pi/2 or \displaystyle u=3\pi/2, in which case \displaystyle u and \displaystyle \pi-u correspond to the same direction and there is only one angle v which satisfies the equality.)
We obtain all the angles v which satisfy (*) by adding multiples of \displaystyle 2\pi,
where n is an arbitrary integer.
If we now go back to our equation
the reasoning above shows that the equation is only satisfied when
If we make x the subject of each equation, we obtain the full solution to the equation,