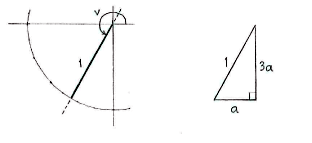Lösung 4.3:6c
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
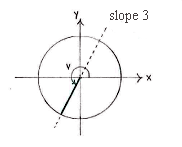
Because the angle \displaystyle v satisfies \displaystyle \pi \le v\le \frac{3\pi }{2}, \displaystyle v belongs to the third quadrant in the unit circle. Furthermore, \displaystyle \text{tan }v=\text{3 } gives that the line which corresponds to the angle \displaystyle v
\displaystyle v has a gradient of \displaystyle \text{3}.
slope 3
In the third quadrant, we can introduce a right-angled triangle in which the hypotenuse is
\displaystyle \text{1}
and the sides have a
\displaystyle \text{3}:\text{1 }
ratio.
If we now use Pythagoras' theorem on the triangle, we see that the horizontal side \displaystyle \text{a} satisfies
\displaystyle a^{2}+\left( 3a \right)^{2}=1^{2}
which gives us that
\displaystyle 10a^{2}=1
i.e.
\displaystyle a=\frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}
Thus, the angle
\displaystyle v's
\displaystyle x
-coordinate is
\displaystyle -\frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}
and
\displaystyle y
-coordinate is
\displaystyle -\frac{3}{\sqrt{10}}, i.e.
\displaystyle \cos v=--\frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}
\displaystyle \sin v=-\frac{3}{\sqrt{10}}