Lösung 2.3:9b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
K |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | Die Schnittpunkte sind die Punkte die auf der Parabel und auf der ''x''-Achse liegen, und also die beiden Gleichungen <math>y=x^{2}-5x+6</math> und <math>y=0</math> erfüllen | + | Die Schnittpunkte sind die Punkte, die auf der Parabel und auf der ''x''-Achse liegen, und also die beiden Gleichungen <math>y=x^{2}-5x+6</math> und <math>y=0</math> erfüllen: |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\left\{\begin{align} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\left\{\begin{align} | ||
| Zeile 6: | Zeile 6: | ||
\end{align}\right.</math>}} | \end{align}\right.</math>}} | ||
| - | Wir | + | Wir erhalten direkt, dass <math>y=0</math> und dass <math>x</math> die Gleichung <math>x^{2}-5x+6=0\,</math> erfüllt. Durch quadratische Ergänzung erhalten wir |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} | ||
| Zeile 14: | Zeile 14: | ||
\end{align}</math>}} | \end{align}</math>}} | ||
| - | Dies | + | Dies ergibt die Lösungen <math>x=\tfrac{5}{2}\pm\tfrac{1}{2}</math>, also <math>x=\tfrac{5}{2}-\tfrac{1}{2}=\tfrac{4}{2}=2</math> und <math>x=\tfrac{5}{2}+\tfrac{1}{2}=\tfrac{6}{2}=3</math>. |
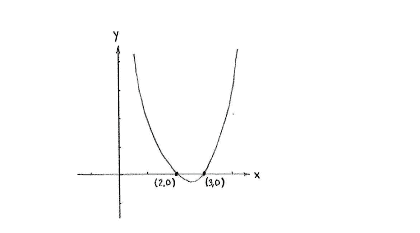
| - | Die Schnittpunkte | + | Die Schnittpunkte sind also (2,0) und (3,0). |
<center>[[Image:2_3_9b-2(2).gif]]</center> | <center>[[Image:2_3_9b-2(2).gif]]</center> | ||
Version vom 14:03, 9. Jun. 2009
Die Schnittpunkte sind die Punkte, die auf der Parabel und auf der x-Achse liegen, und also die beiden Gleichungen \displaystyle y=x^{2}-5x+6 und \displaystyle y=0 erfüllen:
| \displaystyle \left\{\begin{align}
y&=x^{2}-5x+6\,,\\ y&=0\,\textrm{.} \end{align}\right. |
Wir erhalten direkt, dass \displaystyle y=0 und dass \displaystyle x die Gleichung \displaystyle x^{2}-5x+6=0\, erfüllt. Durch quadratische Ergänzung erhalten wir
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
x^{2} - 5x + 6 &= \Bigl(x-\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} - \Bigl(\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} + 6\\[5pt] &= \Bigl(x-\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} - \frac{25}{4} + \frac{24}{4}\\[5pt] &= \Bigl(x-\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} - \frac{1}{4} \end{align} |
Dies ergibt die Lösungen \displaystyle x=\tfrac{5}{2}\pm\tfrac{1}{2}, also \displaystyle x=\tfrac{5}{2}-\tfrac{1}{2}=\tfrac{4}{2}=2 und \displaystyle x=\tfrac{5}{2}+\tfrac{1}{2}=\tfrac{6}{2}=3.
Die Schnittpunkte sind also (2,0) und (3,0).