Lösung 4.4:5b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (hat „Solution 4.4:5b“ nach „Lösung 4.4:5b“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | + | Wir betrachten zuerst die Gleichung | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\tan u=\tan v</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\tan u=\tan v</math>}} | ||
| - | + | Diese Gleichungist erfüllt wenn | |
| - | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>v=u\qquad\text{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>v=u\qquad\text{und}\qquad v=u+\pi\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
[[Image:4_4_5_b.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_5_b.gif|center]] | ||
| - | + | Die allgemeine Lösung ist | |
| - | + | ||
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>v=u+n\pi\,,</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>v=u+n\pi\,,</math>}} | ||
| - | + | Für unsere Gleichung | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\tan x=\tan 4x</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\tan x=\tan 4x</math>}} | ||
| - | + | erhalten wir die Lösungen | |
| - | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>4x = x+n\pi | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>4x = x+n\pi </math>}} |
| - | + | Lösen wir diese Gleichung für ''x'' erhalten wir | |
| - | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x = \tfrac{1}{3}n\pi | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x = \tfrac{1}{3}n\pi</math>}} |
Version vom 11:18, 7. Apr. 2009
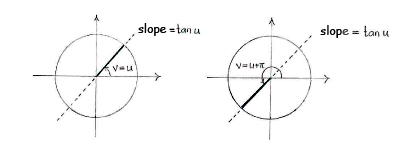
Wir betrachten zuerst die Gleichung
| \displaystyle \tan u=\tan v |
Diese Gleichungist erfüllt wenn
| \displaystyle v=u\qquad\text{und}\qquad v=u+\pi\,\textrm{.} |
Die allgemeine Lösung ist
| \displaystyle v=u+n\pi\,, |
Für unsere Gleichung
| \displaystyle \tan x=\tan 4x |
erhalten wir die Lösungen
| \displaystyle 4x = x+n\pi |
Lösen wir diese Gleichung für x erhalten wir
| \displaystyle x = \tfrac{1}{3}n\pi |