Lösung 4.3:2b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (hat „Solution 4.3:2b“ nach „Lösung 4.3:2b“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | + | Schreiben wir <math>\frac{7\pi }{5}</math> wie | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\frac{7\pi}{5} = \frac{5\pi+2\pi}{5} = \pi + \frac{2\pi }{5}</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\frac{7\pi}{5} = \frac{5\pi+2\pi}{5} = \pi + \frac{2\pi }{5}</math>}} | ||
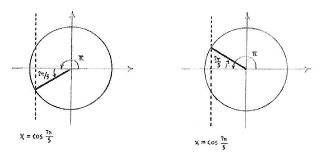
| - | + | sehen wir dass <math>7\pi/5</math> im dritten Quadrant liegt. | |
[[Image:4_3_2_b.gif||center]] | [[Image:4_3_2_b.gif||center]] | ||
| - | + | Der Winkel zwischen <math>0</math> und <math>\pi</math> der dieselbe ''x''-Koordinate wie <math>7\pi/5</math> hat, und daher denselben Kosinus hat, ist die Spiegelung von <math>7\pi/5</math> in der ''x''-Achse, nämlich | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>v = \pi -\frac{2\pi}{5} = \frac{3\pi}{5}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>v = \pi -\frac{2\pi}{5} = \frac{3\pi}{5}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
Version vom 11:35, 5. Apr. 2009
Schreiben wir \displaystyle \frac{7\pi }{5} wie
| \displaystyle \frac{7\pi}{5} = \frac{5\pi+2\pi}{5} = \pi + \frac{2\pi }{5} |
sehen wir dass \displaystyle 7\pi/5 im dritten Quadrant liegt.
Der Winkel zwischen \displaystyle 0 und \displaystyle \pi der dieselbe x-Koordinate wie \displaystyle 7\pi/5 hat, und daher denselben Kosinus hat, ist die Spiegelung von \displaystyle 7\pi/5 in der x-Achse, nämlich
| \displaystyle v = \pi -\frac{2\pi}{5} = \frac{3\pi}{5}\,\textrm{.} |