Lösung 2.2:5d
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (hat „Solution 2.2:5d“ nach „Lösung 2.2:5d“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | + | Wenn zwei nicht-senkrechte Geraden winkelrecht sind, gilt für deren Steigungen <math>k_{1}</math> und <math>k_{2}</math>, dass <math>k_{1}k_{2}=-1</math>, und daher erhalten wir die Steigung von unser Geraden als | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>k_{2} = -\frac{1}{k_{1}} = -\frac{1}{2}</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>k_{2} = -\frac{1}{k_{1}} = -\frac{1}{2}</math>}} | ||
| - | + | Nachdem die Gerade <math>y=2x+5</math> die Steigung <math>k_{1}=2</math> hat. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Also ist die Gleichung unserer Gerade | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y=-\frac{1}{2}x+m</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y=-\frac{1}{2}x+m</math>}} | ||
| - | + | wo ''m'' noch bestimmt werden muss. | |
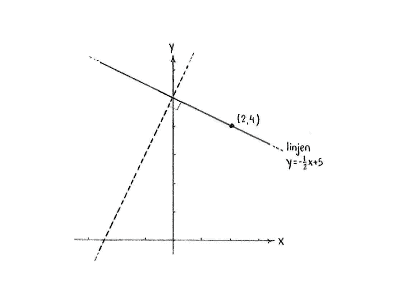
| - | + | Nachdem der Punkt (2,4) auf der Gerade liegt, muss der Punkt (2,4) die Gleichung der Gerade erfüllen | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>4=-\frac{1}{2}\cdot 2+m\,,</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>4=-\frac{1}{2}\cdot 2+m\,,</math>}} | ||
| - | + | Also ist <math>m=5</math>. Die Gleichung der Gerade ist daher <math>y=-\frac{1}{2}x+5</math>. | |
<center>[[Image:2_2_5d-2(2).gif]]</center> | <center>[[Image:2_2_5d-2(2).gif]]</center> | ||
Version vom 11:12, 13. Mär. 2009
Wenn zwei nicht-senkrechte Geraden winkelrecht sind, gilt für deren Steigungen \displaystyle k_{1} und \displaystyle k_{2}, dass \displaystyle k_{1}k_{2}=-1, und daher erhalten wir die Steigung von unser Geraden als
| \displaystyle k_{2} = -\frac{1}{k_{1}} = -\frac{1}{2} |
Nachdem die Gerade \displaystyle y=2x+5 die Steigung \displaystyle k_{1}=2 hat.
Also ist die Gleichung unserer Gerade
| \displaystyle y=-\frac{1}{2}x+m |
wo m noch bestimmt werden muss.
Nachdem der Punkt (2,4) auf der Gerade liegt, muss der Punkt (2,4) die Gleichung der Gerade erfüllen
| \displaystyle 4=-\frac{1}{2}\cdot 2+m\,, |
Also ist \displaystyle m=5. Die Gleichung der Gerade ist daher \displaystyle y=-\frac{1}{2}x+5.