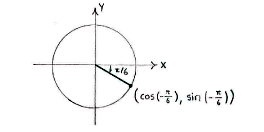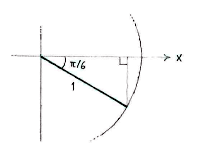Lösung 4.2:3f
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (hat „Solution 4.2:3f“ nach „Lösung 4.2:3f“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | + | Der Punkt auf den Einheitskreis der den Winkel <math>-\pi/6</math> entspricht liegt im vierten Quadrant. | |
[[Image:4_2_3_f1.gif||center]] | [[Image:4_2_3_f1.gif||center]] | ||
| - | + | Wir betrachten ein Dreieck im vierten Quadrant | |
[[Image:4_2_3_f2.gif||center]] | [[Image:4_2_3_f2.gif||center]] | ||
| - | + | Wir berechnen zuerst die Katheten des Dreieckes, und danach die Koordinaten des Punktes. | |
{| width="100%" | {| width="100%" | ||
|width="50%" align="center"|[[Image:4_2_3_f3.gif]] | |width="50%" align="center"|[[Image:4_2_3_f3.gif]] | ||
| - | |width="50%" align="left"|<math>\begin{align}\text{ | + | |width="50%" align="left"|<math>\begin{align}\text{Gegenkathete} &= 1\cdot\sin\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{1}{2}\\[5pt] \text{Ankathete} &= 1\cdot\cos\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{align}</math> |
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | Die Koordinaten des Punktes auf den Einheitskreis entsprechend den Winkel <math>-\pi/6</math> sind also <math>(\sqrt{3}/2,-1/2)</math> und besonders ist <math>\cos (-\pi/6) = \sqrt{3}/2\,</math>. | |
Version vom 14:29, 4. Apr. 2009
Der Punkt auf den Einheitskreis der den Winkel \displaystyle -\pi/6 entspricht liegt im vierten Quadrant.
Wir betrachten ein Dreieck im vierten Quadrant
Wir berechnen zuerst die Katheten des Dreieckes, und danach die Koordinaten des Punktes.
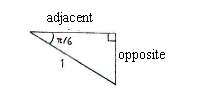
| \displaystyle \begin{align}\text{Gegenkathete} &= 1\cdot\sin\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{1}{2}\\[5pt] \text{Ankathete} &= 1\cdot\cos\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{align} |
Die Koordinaten des Punktes auf den Einheitskreis entsprechend den Winkel \displaystyle -\pi/6 sind also \displaystyle (\sqrt{3}/2,-1/2) und besonders ist \displaystyle \cos (-\pi/6) = \sqrt{3}/2\,.