Lösung 2.3:6a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (hat „Solution 2.3:6a“ nach „Lösung 2.3:6a“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | + | Mit der binomischen Formel <math>(a+b)^2=a^2+2ab+b^2</math>, sehen wir dass der quadratischer Ausdruch <math>(x-1)^{2}\,</math> ist | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x^{2}-2x+1 = (x-1)^{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x^{2}-2x+1 = (x-1)^{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
| - | + | Die Funktion nimmt ihren kleinsten Wert, null an, wenn <math>x-1=0</math>, also wenn | |
| - | <math>x=1</math>. | + | <math>x=1</math>. Alle anderen Werten von <math>x-1</math> ergeben einen positiven Ausdruck <math>(x-1)^{2}</math>. |
| - | <math>(x-1)^{2}</math>. | + | |
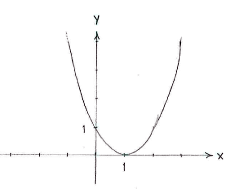
| - | + | Hinweis: Zeichnen wir die Graphe von <math>y=(x-1)^{2}</math>, sehen wir dass die Funktion ein Minimum in <math>x=1\,</math> hat. | |
[[Image:2_3_6_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:2_3_6_a.gif|center]] | ||
Version vom 17:06, 16. Mär. 2009
Mit der binomischen Formel \displaystyle (a+b)^2=a^2+2ab+b^2, sehen wir dass der quadratischer Ausdruch \displaystyle (x-1)^{2}\, ist
| \displaystyle x^{2}-2x+1 = (x-1)^{2}\,\textrm{.} |
Die Funktion nimmt ihren kleinsten Wert, null an, wenn \displaystyle x-1=0, also wenn \displaystyle x=1. Alle anderen Werten von \displaystyle x-1 ergeben einen positiven Ausdruck \displaystyle (x-1)^{2}.
Hinweis: Zeichnen wir die Graphe von \displaystyle y=(x-1)^{2}, sehen wir dass die Funktion ein Minimum in \displaystyle x=1\, hat.