Lösung 4.2:3d
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
In order to get an angle between <math>0</math> and <math>\text{2}\pi</math>, we subtract <math>2\pi</math> from <math>{7\pi }/{2}\,</math>, which also leaves the cosine value unchanged | In order to get an angle between <math>0</math> and <math>\text{2}\pi</math>, we subtract <math>2\pi</math> from <math>{7\pi }/{2}\,</math>, which also leaves the cosine value unchanged | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\cos\frac{7\pi}{2} = \cos\Bigl(\frac{7\pi}{2}-2\pi\Bigr) = \cos\frac{3\pi}{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
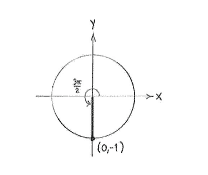
When we draw a line which makes an angle <math>3\pi/2</math> with the positive ''x''-axis, we get the negative ''y''-axis and we see that this line cuts the unit circle at the point (0,-1). The ''x''-coordinate of the intersection point is thus | When we draw a line which makes an angle <math>3\pi/2</math> with the positive ''x''-axis, we get the negative ''y''-axis and we see that this line cuts the unit circle at the point (0,-1). The ''x''-coordinate of the intersection point is thus | ||
Version vom 08:51, 22. Okt. 2008
In order to get an angle between \displaystyle 0 and \displaystyle \text{2}\pi, we subtract \displaystyle 2\pi from \displaystyle {7\pi }/{2}\,, which also leaves the cosine value unchanged
| \displaystyle \cos\frac{7\pi}{2} = \cos\Bigl(\frac{7\pi}{2}-2\pi\Bigr) = \cos\frac{3\pi}{2}\,\textrm{.} |
When we draw a line which makes an angle \displaystyle 3\pi/2 with the positive x-axis, we get the negative y-axis and we see that this line cuts the unit circle at the point (0,-1). The x-coordinate of the intersection point is thus \displaystyle 0 and hence \displaystyle \cos (7\pi/2) = \cos (3\pi/2) = 0\,.