Lösung 4.1:7c
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
By completing the square, we can rewrite the ''x''- and ''y''-terms as quadratic expressions, | By completing the square, we can rewrite the ''x''- and ''y''-terms as quadratic expressions, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} |
x^2 - 2x &= (x-1)^2 - 1^2\,,\\[5pt] | x^2 - 2x &= (x-1)^2 - 1^2\,,\\[5pt] | ||
y^2 + 6y &= (y+3)^2 - 3^2\,, | y^2 + 6y &= (y+3)^2 - 3^2\,, | ||
| Zeile 8: | Zeile 8: | ||
and the whole equation then has standard form, | and the whole equation then has standard form, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} |
(x-1)^2 - 1 + (y+3)^2 - 9 &= -3\,,\\[5pt] | (x-1)^2 - 1 + (y+3)^2 - 9 &= -3\,,\\[5pt] | ||
(x-1)^2 + (y+3)^2 &= 7\,\textrm{.} | (x-1)^2 + (y+3)^2 &= 7\,\textrm{.} | ||
Version vom 08:49, 22. Okt. 2008
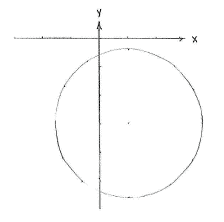
By completing the square, we can rewrite the x- and y-terms as quadratic expressions,
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
x^2 - 2x &= (x-1)^2 - 1^2\,,\\[5pt] y^2 + 6y &= (y+3)^2 - 3^2\,, \end{align} |
and the whole equation then has standard form,
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
(x-1)^2 - 1 + (y+3)^2 - 9 &= -3\,,\\[5pt] (x-1)^2 + (y+3)^2 &= 7\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |
From this, we see that the circle has its centre at (1,-3) and radius \displaystyle \sqrt{7}\,.