Lösung 4.4:2f
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
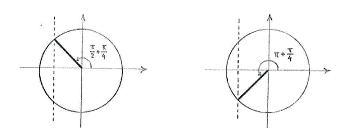
| - | Using the unit circle shows that the equation | + | Using the unit circle shows that the equation <math>\cos 3x = -1/\!\sqrt{2}</math> |
| - | <math>\ | + | has two solutions for <math>0\le 3x\le 2\pi\,</math>, |
| - | has two solutions for | + | |
| - | <math>0\le | + | |
| - | + | {{Displayed math||<math>3x = \frac{\pi}{2} + \frac{\pi}{4} = \frac{3\pi}{4}\qquad\text{and}\qquad 3x = \pi + \frac{\pi}{4} = \frac{5\pi}{4}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | |
| - | <math>3x=\frac{\pi }{2}+\frac{\pi }{4}=\frac{3\pi }{4} | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Image:4_4_2_f.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_2_f.gif|center]] | ||
| - | We obtain the other solutions by adding multiples of | + | We obtain the other solutions by adding multiples of <math>2\pi</math>, |
| - | <math>2\pi </math>, | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>3x = \frac{3\pi}{4} + 2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad 3x = \frac{5\pi}{4} + 2n\pi\,,</math>}} | ||
i.e. | i.e. | ||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>x = \frac{\pi}{4} + \frac{2}{3}n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad x = \frac{5\pi}{12} + \frac{2}{3}n\pi\,,</math>}} | ||
| - | + | where ''n'' is an arbitrary integer. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | where | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | is an arbitrary integer. | + | |
Version vom 12:44, 13. Okt. 2008
Using the unit circle shows that the equation \displaystyle \cos 3x = -1/\!\sqrt{2} has two solutions for \displaystyle 0\le 3x\le 2\pi\,,
We obtain the other solutions by adding multiples of \displaystyle 2\pi,
i.e.
where n is an arbitrary integer.