Lösung 2.3:6a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
Using the rule <math>(a+b)^2=a^2+2ab+b^2</math>, we recognize the polynomial as the expansion of <math>(x-1)^{2}\,</math>, | Using the rule <math>(a+b)^2=a^2+2ab+b^2</math>, we recognize the polynomial as the expansion of <math>(x-1)^{2}\,</math>, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x^{2}-2x+1 = (x-1)^{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
This quadratic expression has its smallest value, zero, when <math>x-1=0</math>, i.e. | This quadratic expression has its smallest value, zero, when <math>x-1=0</math>, i.e. | ||
Version vom 08:33, 22. Okt. 2008
Using the rule \displaystyle (a+b)^2=a^2+2ab+b^2, we recognize the polynomial as the expansion of \displaystyle (x-1)^{2}\,,
| \displaystyle x^{2}-2x+1 = (x-1)^{2}\,\textrm{.} |
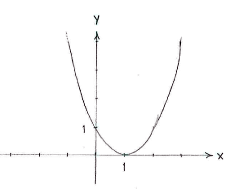
This quadratic expression has its smallest value, zero, when \displaystyle x-1=0, i.e. \displaystyle x=1. All non-zero values of \displaystyle x-1 give a positive value for \displaystyle (x-1)^{2}.
Note: If we draw the curve \displaystyle y=(x-1)^{2}, we see that it has a minimum value of zero at \displaystyle x=1\,.