Lösung 2.3:9c
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
K (Lösning 2.3:9c moved to Solution 2.3:9c: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | { | + | To determine all the points on the curve |
| - | < | + | <math>y=3x^{2}-12x+9</math> |
| - | {{ | + | which also lie on the |
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis we substitute the equation of the | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis i.e. | ||
| + | <math>y=0</math> | ||
| + | in the equation of the curve and obtain that | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | must satisfy | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>3x^{2}-12x+9=0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | After dividing by | ||
| + | <math>3</math> | ||
| + | and completing the square the right-hand side is | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x^{2}-4x+3=\left( x-2 \right)^{2}-2^{2}+3=\left( x-2 \right)^{2}-1</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | and thus the equation has solutions | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x=2\pm 1,</math> | ||
| + | i.e. | ||
| + | <math>x=2-1=1</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>x=2+1=3.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
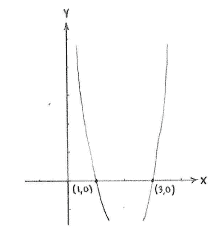
| + | The points where the curve cut the | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis are | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\left( 1 \right.,\left. 0 \right)</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\left( 3 \right.,\left. 0 \right)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:2_3_9_c.gif|center]] | [[Image:2_3_9_c.gif|center]] | ||
Version vom 12:11, 21. Sep. 2008
To determine all the points on the curve \displaystyle y=3x^{2}-12x+9 which also lie on the \displaystyle x -axis we substitute the equation of the \displaystyle x -axis i.e. \displaystyle y=0 in the equation of the curve and obtain that \displaystyle x must satisfy
\displaystyle 3x^{2}-12x+9=0
After dividing by
\displaystyle 3
and completing the square the right-hand side is
\displaystyle x^{2}-4x+3=\left( x-2 \right)^{2}-2^{2}+3=\left( x-2 \right)^{2}-1
and thus the equation has solutions
\displaystyle x=2\pm 1,
i.e.
\displaystyle x=2-1=1
and
\displaystyle x=2+1=3.
The points where the curve cut the
\displaystyle x
-axis are
\displaystyle \left( 1 \right.,\left. 0 \right)
and
\displaystyle \left( 3 \right.,\left. 0 \right)