Lösung 4.4:3b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (hat „Solution 4.4:3b“ nach „Lösung 4.4:3b“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
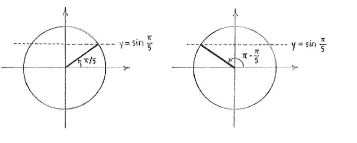
| - | + | <math>x = \pi/5</math> ist eine Lösung der Gleichung, und durch den Einheitskreis sehan wir dass <math>x = \pi - \pi/5 = 4\pi/5</math> die zweite Lösung ist. | |
[[Image:4_4_3_b.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_3_b.gif|center]] | ||
| - | + | Wir erhalten die allgemeine Lösung idem wir einen Multipel von <math>2\pi\, </math> zur Lösung addieren, | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x = \frac{\pi}{5} + 2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad x = \frac{4\pi}{5} + 2n\pi\,,</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x = \frac{\pi}{5} + 2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad x = \frac{4\pi}{5} + 2n\pi\,,</math>}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | where ''n'' is an arbitrary integer. | ||
Version vom 09:20, 7. Apr. 2009
\displaystyle x = \pi/5 ist eine Lösung der Gleichung, und durch den Einheitskreis sehan wir dass \displaystyle x = \pi - \pi/5 = 4\pi/5 die zweite Lösung ist.
Wir erhalten die allgemeine Lösung idem wir einen Multipel von \displaystyle 2\pi\, zur Lösung addieren,
| \displaystyle x = \frac{\pi}{5} + 2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad x = \frac{4\pi}{5} + 2n\pi\,, |