Lösung 4.3:5
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (hat „Solution 4.3:5“ nach „Lösung 4.3:5“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
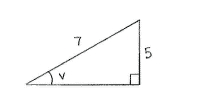
| - | + | Nachdem ''v'' ein scharfer Winkel ist, können wir den Winkel in einen rechtwinkligen Dreieck einzeichnen, wo <math>\sin v = 5/7\,</math>. | |
[[Image:4_3_5_1.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_3_5_1.gif|center]] | ||
| - | + | Dirch das Gesetz des Pythagoras erhalten wir die Länge der unbekannten Seite des Dreiecks. | |
{| align="center" | {| align="center" | ||
||[[Image:4_3_5_2.gif]] | ||[[Image:4_3_5_2.gif]] | ||
| - | ||<math>\begin{align}&x^2 + 5^2 = 7^2\\[5pt] &\text{ | + | ||<math>\begin{align}&x^2 + 5^2 = 7^2\\[5pt] &\text{und wir erhalten}\\[5pt] &x = \sqrt{7^2-5^2} = \sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6}\end{align}</math> |
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | Durch die Definitionen von Kosinus und Tangens erhalten wir | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} | ||
| Zeile 16: | Zeile 16: | ||
\tan v &= \frac{5}{x} = \frac{5}{2\sqrt{6}}\,\textrm{.} | \tan v &= \frac{5}{x} = \frac{5}{2\sqrt{6}}\,\textrm{.} | ||
\end{align}</math>}} | \end{align}</math>}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | Note: The right-angled triangle that we use is just a tool and has nothing to do with the triangle that is referred to in the question. | ||
Version vom 12:35, 5. Apr. 2009
Nachdem v ein scharfer Winkel ist, können wir den Winkel in einen rechtwinkligen Dreieck einzeichnen, wo \displaystyle \sin v = 5/7\,.
Dirch das Gesetz des Pythagoras erhalten wir die Länge der unbekannten Seite des Dreiecks.
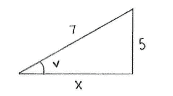
| \displaystyle \begin{align}&x^2 + 5^2 = 7^2\\[5pt] &\text{und wir erhalten}\\[5pt] &x = \sqrt{7^2-5^2} = \sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6}\end{align} |
Durch die Definitionen von Kosinus und Tangens erhalten wir
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
\cos v &= \frac{x}{7} = \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{7}\,,\\[5pt] \tan v &= \frac{5}{x} = \frac{5}{2\sqrt{6}}\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |