Lösung 2.3:9b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
K (hat „Solution 2.3:9b“ nach „Lösung 2.3:9b“ verschoben: Robot: moved page) |
Version vom 14:15, 22. Okt. 2008
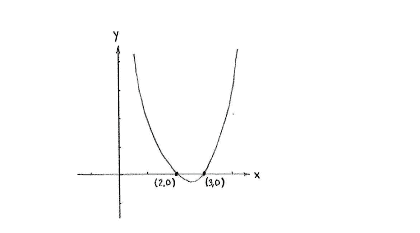
The points of intersection are those points on the curve which also lie on the x-axis, i.e. they are those points which satisfy both the equation of the curve \displaystyle y=x^{2}-5x+6 and the equation of the x-axis \displaystyle y=0,
| \displaystyle \left\{\begin{align}
y&=x^{2}-5x+6\,,\\ y&=0\,\textrm{.} \end{align}\right. |
This system of equations gives directly that \displaystyle y=0 and that \displaystyle x must satisfy the quadratic equation \displaystyle x^{2}-5x+6=0\,. By completing the square, we obtain that the left-hand side is
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
x^{2} - 5x + 6 &= \Bigl(x-\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} - \Bigl(\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} + 6\\[5pt] &= \Bigl(x-\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} - \frac{25}{4} + \frac{24}{4}\\[5pt] &= \Bigl(x-\frac{5}{2}\Bigr)^{2} - \frac{1}{4} \end{align} |
and this gives that the equation has solutions \displaystyle x=\tfrac{5}{2}\pm\tfrac{1}{2}, i.e. \displaystyle x=\tfrac{5}{2}-\tfrac{1}{2}=\tfrac{4}{2}=2 and \displaystyle x=\tfrac{5}{2}+\tfrac{1}{2}=\tfrac{6}{2}=3.
The intersection points are therefore (2,0) and (3,0).