Lösung 4.1:5b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
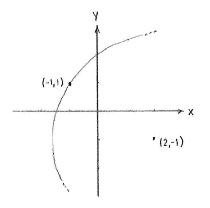
If the circle is to contain the point (-1,1), then that point's distance away from the centre (2,-1) must equal the circle's radius, ''r''. Thus, we can obtain the circle's radius by calculating the distance between (-1,1) and (2,-1) using the distance formula, | If the circle is to contain the point (-1,1), then that point's distance away from the centre (2,-1) must equal the circle's radius, ''r''. Thus, we can obtain the circle's radius by calculating the distance between (-1,1) and (2,-1) using the distance formula, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} |
r &= \sqrt{(2-(-1))^2+(-1-1)^2} = \sqrt{3^2+(-2)^2} = \sqrt{9+4} = \sqrt{13}\,\textrm{.} | r &= \sqrt{(2-(-1))^2+(-1-1)^2} = \sqrt{3^2+(-2)^2} = \sqrt{9+4} = \sqrt{13}\,\textrm{.} | ||
\end{align}</math>}} | \end{align}</math>}} | ||
| Zeile 7: | Zeile 7: | ||
When we know the circle's centre and its radius, we can write the equation of the circle, | When we know the circle's centre and its radius, we can write the equation of the circle, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>(x-2)^2 + (y-(-1))^2 = (\sqrt{13})^{2}</math>}} |
which the same as | which the same as | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>(x-2)^{2} + (y+1)^2 = 13\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
| Zeile 19: | Zeile 19: | ||
Note: A circle having its centre at (''a'',''b'') and radius ''r'' has the equation | Note: A circle having its centre at (''a'',''b'') and radius ''r'' has the equation | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>(x-a)^2 + (y-b)^2 = r^2\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
Version vom 08:48, 22. Okt. 2008
If the circle is to contain the point (-1,1), then that point's distance away from the centre (2,-1) must equal the circle's radius, r. Thus, we can obtain the circle's radius by calculating the distance between (-1,1) and (2,-1) using the distance formula,
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
r &= \sqrt{(2-(-1))^2+(-1-1)^2} = \sqrt{3^2+(-2)^2} = \sqrt{9+4} = \sqrt{13}\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |
When we know the circle's centre and its radius, we can write the equation of the circle,
| \displaystyle (x-2)^2 + (y-(-1))^2 = (\sqrt{13})^{2} |
which the same as
| \displaystyle (x-2)^{2} + (y+1)^2 = 13\,\textrm{.} |
Note: A circle having its centre at (a,b) and radius r has the equation
| \displaystyle (x-a)^2 + (y-b)^2 = r^2\,\textrm{.} |