Lösung 4.4:2e
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
K (Lösning 4.4:2e moved to Solution 4.4:2e: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
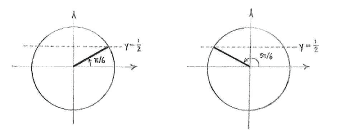
| - | {{ | + | This is almost the same equation as in exercise d. First, we determine the solutions to the equation |
| - | < | + | when |
| - | {{ | + | <math>0\le \text{5}x\le \text{2}\pi </math>, and using the unit circle shows that there are two of these: |
| + | <math>\text{5}x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{6}</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\text{5}x\text{ }=\pi -\frac{\pi }{6}=\frac{5\pi }{6}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:4_4_2_e.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_2_e.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We obtain the remaining solutions by adding multiples of | ||
| + | <math>2\pi </math> | ||
| + | to the two solutions above: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\text{5}x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{6}+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\text{5}x\text{ }=\frac{5\pi }{6}+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | <math>n</math> | ||
| + | an arbitrary integer), | ||
| + | |||
| + | or if we divide by | ||
| + | <math>\text{5}</math>: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{30}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi </math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{6}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi </math> | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | <math>n</math> | ||
| + | an arbitrary integer). | ||
Version vom 08:36, 1. Okt. 2008
This is almost the same equation as in exercise d. First, we determine the solutions to the equation when \displaystyle 0\le \text{5}x\le \text{2}\pi , and using the unit circle shows that there are two of these: \displaystyle \text{5}x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{6} and \displaystyle \text{5}x\text{ }=\pi -\frac{\pi }{6}=\frac{5\pi }{6}.
We obtain the remaining solutions by adding multiples of \displaystyle 2\pi to the two solutions above:
\displaystyle \text{5}x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{6}+2n\pi
and
\displaystyle \text{5}x\text{ }=\frac{5\pi }{6}+2n\pi
(
\displaystyle n
an arbitrary integer),
or if we divide by \displaystyle \text{5}:
\displaystyle x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{30}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi
and
\displaystyle x\text{ }=\frac{\pi }{6}+\frac{2}{5}n\pi
(
\displaystyle n
an arbitrary integer).