Lösung 2.3:6a
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (Lösning 2.3:6a moved to Solution 2.3:6a: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | {{ | + | Using the squaring rule, we recognize the polynomial as the expansion of |
| - | < | + | <math>\left( x-1 \right)^{2}</math>, |
| - | {{ | + | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>x^{2}-2x+1=\left( x-1 \right)^{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This quadratic expression has its smallest value, zero, when | ||
| + | <math>x-\text{1}=0</math>, i.e. | ||
| + | <math>x=\text{1}</math>. All non-zero values of | ||
| + | <math>x-\text{1}</math> | ||
| + | give a positive value for | ||
| + | <math>\left( x-1 \right)^{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
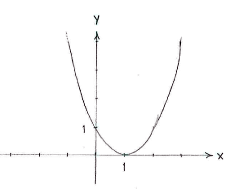
| + | NOTE: If we draw the curve | ||
| + | <math>y=\left( x-1 \right)^{2}</math>, we see that it has a minimum value of zero at | ||
| + | <math>x=\text{1}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:2_3_6_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:2_3_6_a.gif|center]] | ||
Version vom 10:51, 21. Sep. 2008
Using the squaring rule, we recognize the polynomial as the expansion of \displaystyle \left( x-1 \right)^{2},
\displaystyle x^{2}-2x+1=\left( x-1 \right)^{2}
This quadratic expression has its smallest value, zero, when
\displaystyle x-\text{1}=0, i.e.
\displaystyle x=\text{1}. All non-zero values of
\displaystyle x-\text{1}
give a positive value for
\displaystyle \left( x-1 \right)^{2}.
NOTE: If we draw the curve \displaystyle y=\left( x-1 \right)^{2}, we see that it has a minimum value of zero at \displaystyle x=\text{1}.