Lösung 2.2:6b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 1
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (Lösning 2.2:6b moved to Solution 2.2:6b: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| + | Because the point of intersection lies on both lines, it must satisfy the equations of both lines | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>y=-x+5</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>x=0</math>, | ||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | <math>x=0</math> | ||
| + | is the equation of the | ||
| + | <math>y</math> | ||
| + | -axis. Substituting the other equation, | ||
| + | <math>x=0</math>, into the first equation gives | ||
| + | <math>y=-0+5=5</math>. This means that the point of intersection is | ||
| + | <math>\left( 0 \right.,\left. 5 \right)</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{NAVCONTENT_START}} | {{NAVCONTENT_START}} | ||
[[Image:2_2_6_b.gif]] | [[Image:2_2_6_b.gif]] | ||
| - | + | ||
{{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} | {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} | ||
Version vom 10:24, 18. Sep. 2008
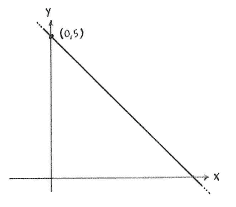
Because the point of intersection lies on both lines, it must satisfy the equations of both lines
\displaystyle y=-x+5
and
\displaystyle x=0,
where \displaystyle x=0 is the equation of the \displaystyle y -axis. Substituting the other equation, \displaystyle x=0, into the first equation gives \displaystyle y=-0+5=5. This means that the point of intersection is \displaystyle \left( 0 \right.,\left. 5 \right).