Solution 4.2:5a
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
(Ny sida: {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:4_2_5a.gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}}) |
m |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
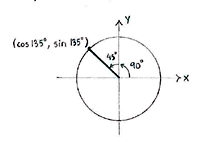
| - | {{ | + | Because <math>135^{\circ} = 90^{\circ} + 45^{\circ}</math>, <math>135^{\circ}</math> is an angle in the second quadrant which makes an angle of <math>45^{\circ}</math> with the positive ''y''-axis. |
| - | < | + | |
| - | {{ | + | [[Image:4_2_5_a1.gif|center]] |
| + | |||
| + | We can determine the point on the unit circle which corresponds to <math>135^{\circ}</math> by introducing an auxiliary triangle and calculating its edges using trigonometry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| width="100%" | ||
| + | |width="50%" align="center"|[[Image:4_2_5_a2.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |width="50%" align="left"|<math>\begin{align}\text{opposite} &= 1\cdot\sin 45^{\circ} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\\[5pt] \text{adjacent} &= 1\cdot\cos 45^{\circ} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The coordinates of the point are <math>( -1/\!\sqrt{2}, 1/\!\sqrt{2})</math> and this shows that <math>\cos 135^{\circ} = -1/\!\sqrt{2}\,</math>. | ||
Current revision
Because \displaystyle 135^{\circ} = 90^{\circ} + 45^{\circ}, \displaystyle 135^{\circ} is an angle in the second quadrant which makes an angle of \displaystyle 45^{\circ} with the positive y-axis.
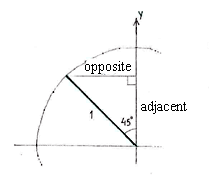
We can determine the point on the unit circle which corresponds to \displaystyle 135^{\circ} by introducing an auxiliary triangle and calculating its edges using trigonometry.
| \displaystyle \begin{align}\text{opposite} &= 1\cdot\sin 45^{\circ} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\\[5pt] \text{adjacent} &= 1\cdot\cos 45^{\circ} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\end{align} |
The coordinates of the point are \displaystyle ( -1/\!\sqrt{2}, 1/\!\sqrt{2}) and this shows that \displaystyle \cos 135^{\circ} = -1/\!\sqrt{2}\,.