Solution 4.2:1a
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
(Ny sida: {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:4_2_1.gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}}) |
m |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {{ | + | The definition of the tangent states that |
| - | < | + | |
| - | {{ | + | {| width="100%" |
| + | | width="50%" align="center"|<math>\tan u=\frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{adjacent}}</math> | ||
| + | | width="50%" align="center"|[[Image:4_2_1_a.gif]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In our case, this means that | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>\tan 27^{\circ} = \frac{x}{13}</math>}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | which gives <math>x = 13\cdot \tan 27^{\circ}\,</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Note: Using a calculator, we can work out what ''x'' should be, | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>x = 13\cdot\tan 27^{\circ} \approx 6\textrm{.}62\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
Current revision
The definition of the tangent states that
| \displaystyle \tan u=\frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{adjacent}} | 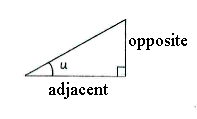
|
In our case, this means that
| \displaystyle \tan 27^{\circ} = \frac{x}{13} |
which gives \displaystyle x = 13\cdot \tan 27^{\circ}\,.
Note: Using a calculator, we can work out what x should be,
| \displaystyle x = 13\cdot\tan 27^{\circ} \approx 6\textrm{.}62\,\textrm{.} |
