Solution 4.3:5
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
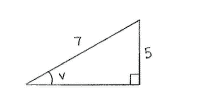
| - | An often-used technique to calculate | + | An often-used technique to calculate <math>\cos v</math> and <math>\tan v</math>, given the sine value of an acute angle, is to draw the angle <math>v</math> in a right-angled triangle which has two sides arranged so that <math>\sin v = 5/7\,</math>. |
| - | <math>\ | + | |
| - | and | + | |
| - | <math>\ | + | |
| - | <math>v</math> | + | |
| - | in a right-angled triangle which has two sides arranged so that | + | |
| - | <math>\ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Image:4_3_5_1.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_3_5_1.gif|center]] | ||
| - | Using | + | Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can determine the length of the third side in the triangle. |
| - | + | {| align="center" | |
| - | [[Image:4_3_5_2.gif | + | ||[[Image:4_3_5_2.gif]] |
| - | + | ||<math>\begin{align}&x^2 + 5^2 = 7^2\\[5pt] &\text{which gives that}\\[5pt] &x = \sqrt{7^2-5^2} = \sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6}\end{align}</math> | |
| - | + | |} | |
| - | <math>x^ | + | |
| - | which gives that | + | |
| - | + | ||
Then, using the definition of cosine and tangent, | Then, using the definition of cosine and tangent, | ||
| - | + | {{Displayed math||<math>\begin{align} | |
| - | <math>\begin{align} | + | \cos v &= \frac{x}{7} = \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{7}\,,\\[5pt] |
| - | + | \tan v &= \frac{5}{x} = \frac{5}{2\sqrt{6}}\,\textrm{.} | |
| - | + | \end{align}</math>}} | |
| - | \end{align}</math> | + | |
| - | + | Note: The right-angled triangle that we use is just a tool and has nothing to do with the triangle that is referred to in the question. | |
Current revision
An often-used technique to calculate \displaystyle \cos v and \displaystyle \tan v, given the sine value of an acute angle, is to draw the angle \displaystyle v in a right-angled triangle which has two sides arranged so that \displaystyle \sin v = 5/7\,.
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can determine the length of the third side in the triangle.
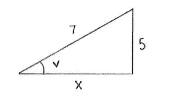
| \displaystyle \begin{align}&x^2 + 5^2 = 7^2\\[5pt] &\text{which gives that}\\[5pt] &x = \sqrt{7^2-5^2} = \sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6}\end{align} |
Then, using the definition of cosine and tangent,
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
\cos v &= \frac{x}{7} = \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{7}\,,\\[5pt] \tan v &= \frac{5}{x} = \frac{5}{2\sqrt{6}}\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |
Note: The right-angled triangle that we use is just a tool and has nothing to do with the triangle that is referred to in the question.