Solution 4.2:3a
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
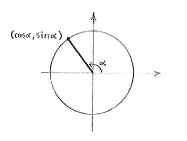
A useful technique for calculating the value of a trigonometric function for angles that don't lie between \displaystyle 0 and \displaystyle {\pi }/{2}\; is to use the unit circle. If we draw a line which starts at the origin and makes a certain angle relative to the positive part of the x-axis, we can see that the cosine of that angle is the x-coordinate of the point of intersection between the line and the unit circle. In the same way, the sine of the angle is the y-coordinate of the intersection point.
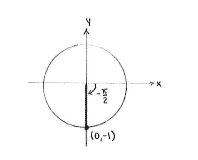
In this case, we see immediately that \displaystyle \sin\Bigl(-\frac{\pi}{2}\Bigr) = -1\,.