Solution 4.3:2b
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
If we write the angle \displaystyle \frac{7\pi }{5} as
\displaystyle \frac{7\pi }{5}=\frac{5\pi +2\pi }{5}=\pi +\frac{2\pi }{5}
we see that
\displaystyle \frac{7\pi }{5}
is an angle in the third quadrant.
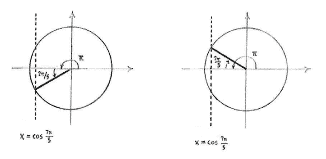
the line
\displaystyle x=\cos \frac{7\pi }{5}
The angle between \displaystyle 0 and \displaystyle \pi which has the same x-coordinate as the angle \displaystyle {7\pi }/{5}\;, and hence the same cosine value, is the reflection of the angle \displaystyle {7\pi }/{5}\; in the \displaystyle x -axis, i.e. \displaystyle v=\pi -\frac{2\pi }{5}=\frac{3\pi }{5}.
