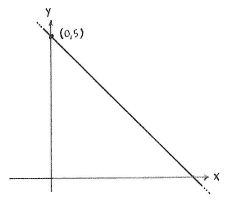
Solution 2.2:6b
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
Because the point of intersection lies on both lines, it must satisfy the equations of both lines
\displaystyle y=-x+5
and
\displaystyle x=0,
where \displaystyle x=0 is the equation of the \displaystyle y -axis. Substituting the other equation, \displaystyle x=0, into the first equation gives \displaystyle y=-0+5=5. This means that the point of intersection is \displaystyle \left( 0 \right.,\left. 5 \right).