Solution 4.4:5c
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
m (Lösning 4.4:5c moved to Solution 4.4:5c: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | For a fixed value of | |
| - | < | + | <math>u</math>, an equality of the form |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | < | + | <math>\cos u=\cos v</math> |
| - | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | is satisfied by two angles | ||
| + | <math>v</math> | ||
| + | in the unit circle: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>v=u</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>v=-u</math> | ||
[[Image:4_4_5_c.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_5_c.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This means that all angles | ||
| + | <math>v</math> | ||
| + | which satisfy the equality are | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>v=u+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>v=-u+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | <math>n\text{ }</math> | ||
| + | is an arbitrary integer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, the equation | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\cos 5x=\cos \left( x+{\pi }/{5}\; \right)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | has the solutions | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>5x=x+\frac{\pi }{5}+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | or | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>5x=-x-\frac{\pi }{5}+2n\pi </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we collect | ||
| + | <math>x\text{ }</math> | ||
| + | onto one side, we end up with | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\left\{ \begin{array}{*{35}l} | ||
| + | x=\frac{\pi }{20}+\frac{1}{2}n\pi \\ | ||
| + | x=-\frac{\pi }{30}+\frac{1}{3}n\pi \\ | ||
| + | \end{array} \right.</math> | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | <math>n\text{ }</math> | ||
| + | an arbitrary integer). | ||
Revision as of 11:18, 1 October 2008
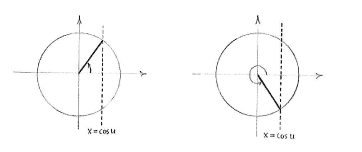
For a fixed value of \displaystyle u, an equality of the form
\displaystyle \cos u=\cos v
is satisfied by two angles
\displaystyle v
in the unit circle:
\displaystyle v=u
and
\displaystyle v=-u
This means that all angles \displaystyle v which satisfy the equality are
\displaystyle v=u+2n\pi
and
\displaystyle v=-u+2n\pi
where
\displaystyle n\text{ }
is an arbitrary integer.
Therefore, the equation
\displaystyle \cos 5x=\cos \left( x+{\pi }/{5}\; \right)
has the solutions
\displaystyle 5x=x+\frac{\pi }{5}+2n\pi
or
\displaystyle 5x=-x-\frac{\pi }{5}+2n\pi
If we collect \displaystyle x\text{ } onto one side, we end up with
\displaystyle \left\{ \begin{array}{*{35}l}
x=\frac{\pi }{20}+\frac{1}{2}n\pi \\
x=-\frac{\pi }{30}+\frac{1}{3}n\pi \\
\end{array} \right.
(
\displaystyle n\text{ }
an arbitrary integer).