Solution 4.1:5b
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
(Ny sida: {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:4_1_5b-1(2).gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:4_1_5b-2(2).gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}}) |
m |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
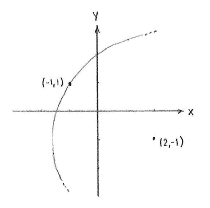
| - | {{ | + | If the circle is to contain the point (-1,1), then that point's distance away from the centre (2,-1) must equal the circle's radius, ''r''. Thus, we can obtain the circle's radius by calculating the distance between (-1,1) and (2,-1) using the distance formula, |
| - | < | + | |
| - | {{ | + | {{Displayed math||<math>\begin{align} |
| - | {{ | + | r &= \sqrt{(2-(-1))^2+(-1-1)^2} = \sqrt{3^2+(-2)^2} = \sqrt{9+4} = \sqrt{13}\,\textrm{.} |
| - | < | + | \end{align}</math>}} |
| - | {{ | + | |
| + | When we know the circle's centre and its radius, we can write the equation of the circle, | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>(x-2)^2 + (y-(-1))^2 = (\sqrt{13})^{2}</math>}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | which the same as | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>(x-2)^{2} + (y+1)^2 = 13\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:4_1_5_b-1(2).gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Note: A circle having its centre at (''a'',''b'') and radius ''r'' has the equation | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>(x-a)^2 + (y-b)^2 = r^2\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
Current revision
If the circle is to contain the point (-1,1), then that point's distance away from the centre (2,-1) must equal the circle's radius, r. Thus, we can obtain the circle's radius by calculating the distance between (-1,1) and (2,-1) using the distance formula,
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
r &= \sqrt{(2-(-1))^2+(-1-1)^2} = \sqrt{3^2+(-2)^2} = \sqrt{9+4} = \sqrt{13}\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |
When we know the circle's centre and its radius, we can write the equation of the circle,
| \displaystyle (x-2)^2 + (y-(-1))^2 = (\sqrt{13})^{2} |
which the same as
| \displaystyle (x-2)^{2} + (y+1)^2 = 13\,\textrm{.} |
Note: A circle having its centre at (a,b) and radius r has the equation
| \displaystyle (x-a)^2 + (y-b)^2 = r^2\,\textrm{.} |