Solution 4.4:1a
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m (Lösning 4.4:1a moved to Solution 4.4:1a: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
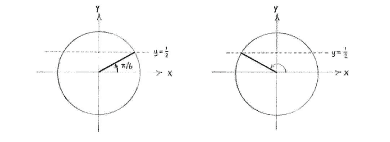
| - | {{ | + | In the unit circle's first quadrant, there is one angle whose sine value equals |
| - | + | <math>\frac{1}{2}</math> | |
| - | {{ | + | and that is |
| + | <math>v={\pi }/{6}\;</math>. | ||
[[Image:4_4_1_a.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_1_a.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the figures, we see that there is a further angle with the same sine value and it lies in the second quadrant. Because of symmetry, it makes the same angle with the negative | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis as | ||
| + | <math>v={\pi }/{6}\;</math> | ||
| + | makes with the positive | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis, i.e. the other angle is | ||
| + | <math>v=\pi -{\pi }/{6}\;={5\pi }/{6}\;</math> | ||
Revision as of 11:58, 30 September 2008
In the unit circle's first quadrant, there is one angle whose sine value equals \displaystyle \frac{1}{2} and that is \displaystyle v={\pi }/{6}\;.
From the figures, we see that there is a further angle with the same sine value and it lies in the second quadrant. Because of symmetry, it makes the same angle with the negative \displaystyle x -axis as \displaystyle v={\pi }/{6}\; makes with the positive \displaystyle x -axis, i.e. the other angle is \displaystyle v=\pi -{\pi }/{6}\;={5\pi }/{6}\;