Solution 2.2:5e
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m (Lösning 2.2:5e moved to Solution 2.2:5e: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
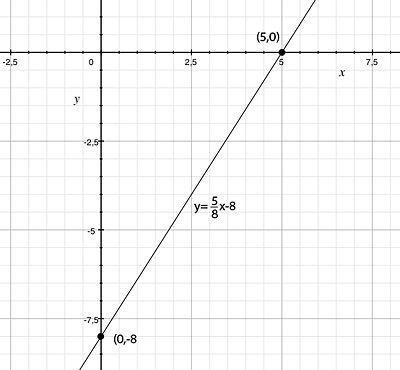
| + | The line should go through the points | ||
| + | <math>\left( 5 \right.,\left. 0 \right)</math> | ||
| + | and | ||
| + | <math>\left( 0 \right.,\left. -8 \right)</math> | ||
| + | which must therefore satisfy the equation of the line | ||
| + | <math>y=kx+m</math>, i.e. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>0=k\centerdot 5+m</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | From the other equation, we get | ||
| + | <math>m=-8</math> | ||
| + | and substituting this into the first equation gives | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>0=5k-8\ \Leftrightarrow \ k={8}/{5}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The gradient of the line is | ||
| + | <math>{8}/{5}\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{NAVCONTENT_START}} | {{NAVCONTENT_START}} | ||
[[Image:S1_2_2_5_e.jpg|400px]] | [[Image:S1_2_2_5_e.jpg|400px]] | ||
<!--<center> [[Image:2_2_5e.gif]] </center>--> | <!--<center> [[Image:2_2_5e.gif]] </center>--> | ||
{{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} | {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} | ||
Revision as of 10:05, 18 September 2008
The line should go through the points \displaystyle \left( 5 \right.,\left. 0 \right) and \displaystyle \left( 0 \right.,\left. -8 \right) which must therefore satisfy the equation of the line \displaystyle y=kx+m, i.e.
\displaystyle 0=k\centerdot 5+m
From the other equation, we get
\displaystyle m=-8
and substituting this into the first equation gives
\displaystyle 0=5k-8\ \Leftrightarrow \ k={8}/{5}\;
The gradient of the line is
\displaystyle {8}/{5}\;.